LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display, referring to the technology behind these popular flat panel monitors. An LCD monitor is distinguishable from a traditional CRT monitor as the latter has a bulky footprint with a depth of several inches and a weight of 30 - 50 pounds (13 - 23 kilograms) or more, while LCDs are commonly 1 - 3 inches (2.5 - 7.5 cm) thick and weigh less than 10 pounds (4.5 k).
LCD displays were used on laptop computers before the technology improved enough to make the jump to desktop monitors. An LCD monitor consists of five layers: a backlight, a sheet of polarized glass, a "mask" of colored pixels, a layer of liquid crystal solution responsive to a wired grid of x, y coordinates, and a second polarized sheet of glass. By manipulating the orientations of crystals through precise electrical charges of varying degrees and voltages, the crystals act like tiny shutters, opening or closing in response to the stimulus, thereby allowing degrees of light that have passed through specific colored pixels to illuminate the screen, creating a picture.
As LCD technology evolves, different techniques for producing color emerge. Active-matrix or TFT (thin film transistor) technology produces color and images as sharp as any CRT and is generally considered superior to passive-matrix technologies.
Important specifications to consider when shopping for an LCD monitor include contrast ratio, brightness (or "nits"), viewing angle, and response time.
Contrast ratio relates to the display's comparative difference between its brightest white values and its darkest black values. A higher contrast ratio will have truer colors with less "wash out." The standard offering for lower end models is commonly 350:1. Many experts recommend a contrast ratio of 500:1 or better.
An LCD monitor is brighter than a CRT, giving the consumer little reason to hunt for an especially bright model. Brightness is measured in nits, or one candela per square meter. Anywhere from 250 - 300 nits is standard. If the nits are much higher you'll likely end up adjusting the brightness way down.
The viewing angle is an especially important consideration if you plan to have multiple people viewing the LCD monitor at any given time. There is a vertical and a horizontal viewing angle specification, which refers to the degree you can stray from dead center before the picture starts to wash out. High contrast levels usually go hand-in-hand with wider viewing angles. Many recommend a viewing angle of at least 140 degrees horizontal and 120 degrees vertical. The wider the viewing angles, the better.
Response time is measured in milliseconds (ms) and refers to how long it takes pixels to turn from completely white to black and back again. Smaller values represent a faster response time and are more desirable, especially for gaming or viewing video. If the response time is slow, "ghosting" or "trailing" can occur with fast-moving images, as repaints of the screen overlap. A maximum response time should be no more than 25ms for general use, and 17ms is better. Many gamers report no ghosting using an LCD monitor with a response time of 16ms or less.
LCDs use only one-third to one-half the electricity of their CRT counterparts. They are much easier on the eyes, take up 90% less space, and only weigh a few pounds. They also emit far less low-frequency radiation than CRTs. This makes LCDs a great choice for nearly everyone, and ideal for people who work all day in front of the screen. Colors may change hue as one moves to the outer limits of the viewing angle, particularly on displays with narrow viewing angles and low contrast ratios. For this reason graphics professionals that require exacting color consistency regardless of viewing angle generally use CRTs, though LCDs have improved in this regard.
An LCD monitor comes in standard sizes from 15-inches to 21-inches, and larger. The viewing screen is the same size as the rated display, unlike CRT monitors. Therefore a 15-inch LCD will have a 15-inch viewing screen.
A potential weak link of an LCD monitor is the backlight. Many monitors come with a 3-year warranty, but stipulate 1 year for the backlight. Models with 3-year warranties that cover the backlight usually cost a little more but may be worth the extra investment.
Reflective twisted nematic liquid crystal display.
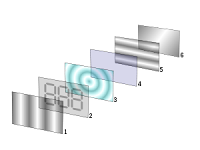
- Polarizing filter film with a vertical axis to polarize light as it enters.
- Glass substrate with ITO electrodes. The shapes of these electrodes will determine the shapes that will appear when the LCD is turned ON. Vertical ridges etched on the surface are smooth.
- Twisted nematic liquid crystal.
- Glass substrate with common electrode film (ITO) with horizontal ridges to line up with the horizontal filter.
- Polarizing filter film with a horizontal axis to block/pass light.
- Reflective surface to send light back to viewer. (In a backlit LCD, this layer is replaced with a light source.)
A liquid crystal display (LCD) is an electro-optical amplitude modulator realized as a thin, flat display device made up of any number of color or monochrome pixels arrayed in front of a light source or reflector. It is often utilized in battery-powered electronic devices because it uses very small amounts of electric power.
A comprehensive classification of the various types and electro-optical modes of LCDs is provided in the article LCD classification.






 10:16 AM
10:16 AM
 PM2 PRINTING
PM2 PRINTING










